It has been well established that siRNA offtarget effects are caused by the seed sequence of the siRNA (bases 2–8 of the guide strand) 7,10 Previous work demonstrated an enrichment of a specific seed region among the top screening hits 23 Furthermore, in Sudbery et al, 9 a statistical test was applied to identify 17 hexamer and 13Minimization of seeddependent offtarget effects siDirect selects siRNAs with lower Tm value at the seed region, which contains 7 nucleotides at positions 28 from 5′ end of the guide strand siRNAs downregulate many unintended genes whose transcripts have complementarities to the siRNA seed region If seed region sequence complementarity is a primary determinant of offtarget transcript regulation, then base mismatches within the seed region that disrupt interaction between siRNA and transcript should alter offtarget silencing
The Sirna Non Seed Region And Its Target Sequences Are Auxiliary Determinants Of Off Target Effects
Seed region sirna
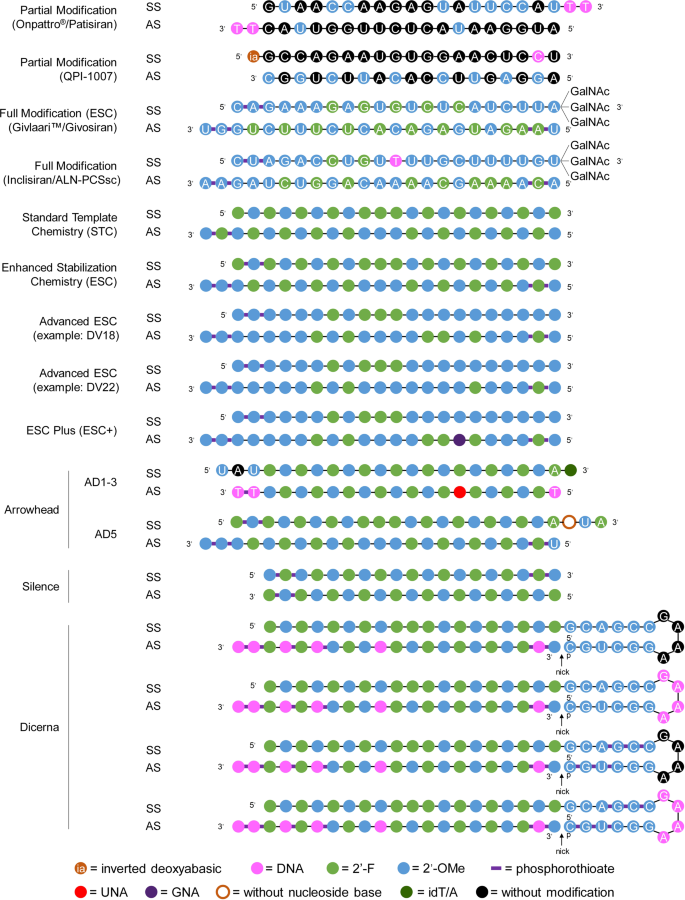
Seed region sirna-Our results confirm previous reports that strength of basepairing in the siRNA seed region is the primary factor determining the efficiency of offtarget silencing However, the degree of downregulation of offtarget transcripts with shared seed sequence is not necessarily similar, suggesting that there are additional auxiliary factors that influence the silencing potentialChemical modifications of 2'Omethyl (2'OMe) and locked nucleic acid (LNA) of the nucleotides in the seed region (positions 28) of the small interfering RNA (siRNA) guide strand significantly reduced seedmatched (SM) offtarget effects The siRNA




Seed And Non Seed Region Dependent Off Target Effect Analyses For Download Scientific Diagram
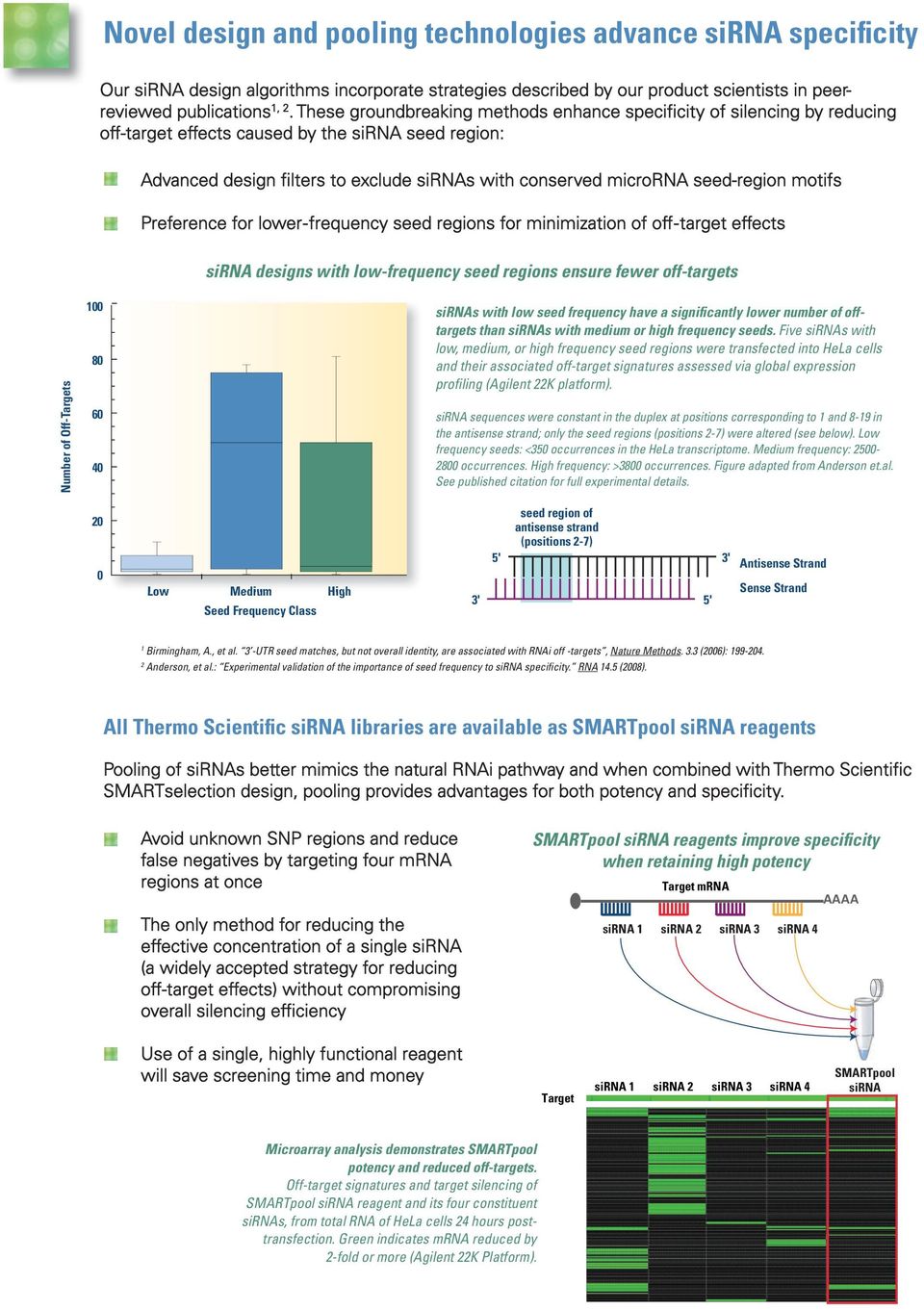
Five siRNAs with low, medium, or high frequency seed regions were transfected into HeLa cells and their associated offtarget signatures assessed via global expression profiling (Agilent 22K platform) siRNA sequences were constant at positions 1 and 819, only the seed regions (positions 27) were altered Interestingly, the three offtarget siRNAs were found to knock down an antiapoptotic l2 family protein Mcl1 owing to the complementation between their seed regions with the 3′ untranslatedFinally, siRNA sequences are ranked according to the frequency of potential siRNA seed region matches to the 3' untranslated region (UTR) of offtarget transcripts Only those siRNAs that have the highest rankings from the siRNA design process, pass all specificity filters, and have the fewest predicted 3' UTR–siRNA seed region matches to off
Clearly, the seed sequences of miRNA (identified with miRNA databases) should be avoided in siRNA design 69 In addition, the siRNA should have a low thermodynamic stability of the duplex between the seed region of the guide strand of siRNA and its target mRNA, since a low seedtarget duplex stability reduces the capability of siRNA to induceScripts with complementarity to the seed region of the siRNA antisense strand When compared to 2amethoxy ribosyl (2aOMe) modified siRNAs previously developed to alleviate antisense offtarget silencing; Base mismatches within the siRNA seed region reduced the set of original offtarget transcripts but generated new sets of silenced transcripts with sequence complementarity to the mismatched seed sequence An inducible shRNA silenced a subset of transcripts that were silenced by an siRNA of the same sequence, demonstrating that unintended silencing is sequence
FAQ ID 2262 miRNAs regulate the gene expression by binding to the mRNA The seed sequence is essential for the binding of the miRNA to the mRNA The seed sequence or seed region is a conserved heptametrical sequence which is mostly situated at positions 27 from the miRNA 5´end Even though base pairing of miRNA and its target mRNA does not match perfect, the "seed (2′S)2′Deoxy2′Cmethyluridine and (2′R)2′deoxy2′Cmethyluridine were incorporated in the 3′overhang region of the sense and antisense strands and in positions 2 and 5 of the seed region of siRNA duplexes directed against Renilla luciferase, whereas (2′S)2′deoxy2′Cmethylcytidine was incorporated in the 6position of the seed region of the same Hence, because the siRNA seed region is a primary targetrecognition region, it is possible that the highly stable seedtarget duplex results in



The Sirna Non Seed Region And Its Target Sequences Are Auxiliary Determinants Of Off Target Effects




Small Interfering Rna Wikipedia
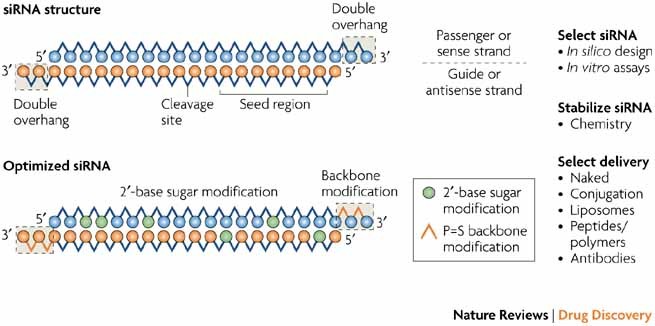
The short length of the seed sequence in the siRNA guide strand together with the high prevalence of heptamer motifs in any genome make the design of monospecific siRNA highly challenging The seed region motifs of F71 (5' CCTATTC 3') and F72 (5' CTTCGAT 3') for instance have 3,260 or 1,3 hits in all RefSeq annotated transcripts and However, as the guide strand of an siRNA can function like a natural microRNA (miRNA), siRNAs often repress hundreds of off‐target transcripts with complementarity only to the seed region (nucleotides 2–8) of the guide strand Here, we describe novel guide strand 3′‐end modifications derived from 1‐ethynylribose (1‐ER) and copperThe seed region of the siRNA Interestingly, the majority of offtargets that were annotated as being involved in immune response were downregulated (Table S3) When the concentration of HK was reduced from 25 nM to 10 nM, there was a 33 fold decrease in HK2 mRNA



Therapeutic Sirna State Of The Art Signal Transduction And Targeted Therapy



Si Rna 13
Seed region The chemical modifications of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), PS, and DNA−PS were introduced into all of the seven nucleotides of the seed region of the siRNA guide strand (Figure 2b) In addition, 3 (positions 4−6), 5 (positions 3−7),MISSION ® Predesigned siRNA were created using the proprietary Rosetta Inpharmatics siRNA Design algorithm in an exclusive partnership with Merck & Co The Rosetta siRNA Design Algorithm utilizes PositionSpecific Scoring Matrices and knowledge of the seed region to predict the most specific and effective sequences for your target genesChemical modifications of 2′Omethyl (2′OMe) and locked nucleic acid (LNA) of the nucleotides in the seed region (positions 2–8) of the small interfering RNA (siRNA) guide strand significantly reduced seedmatched (SM) offtarget effects The siRNA with 2′OMe modifications inhibited the expression of a completelymatched (CM) target gene, whereas that with LNA modifications did



Interfering With Disease A Progress Report On Sirna Based Therapeutics Nature Reviews Drug Discovery



Sidirect
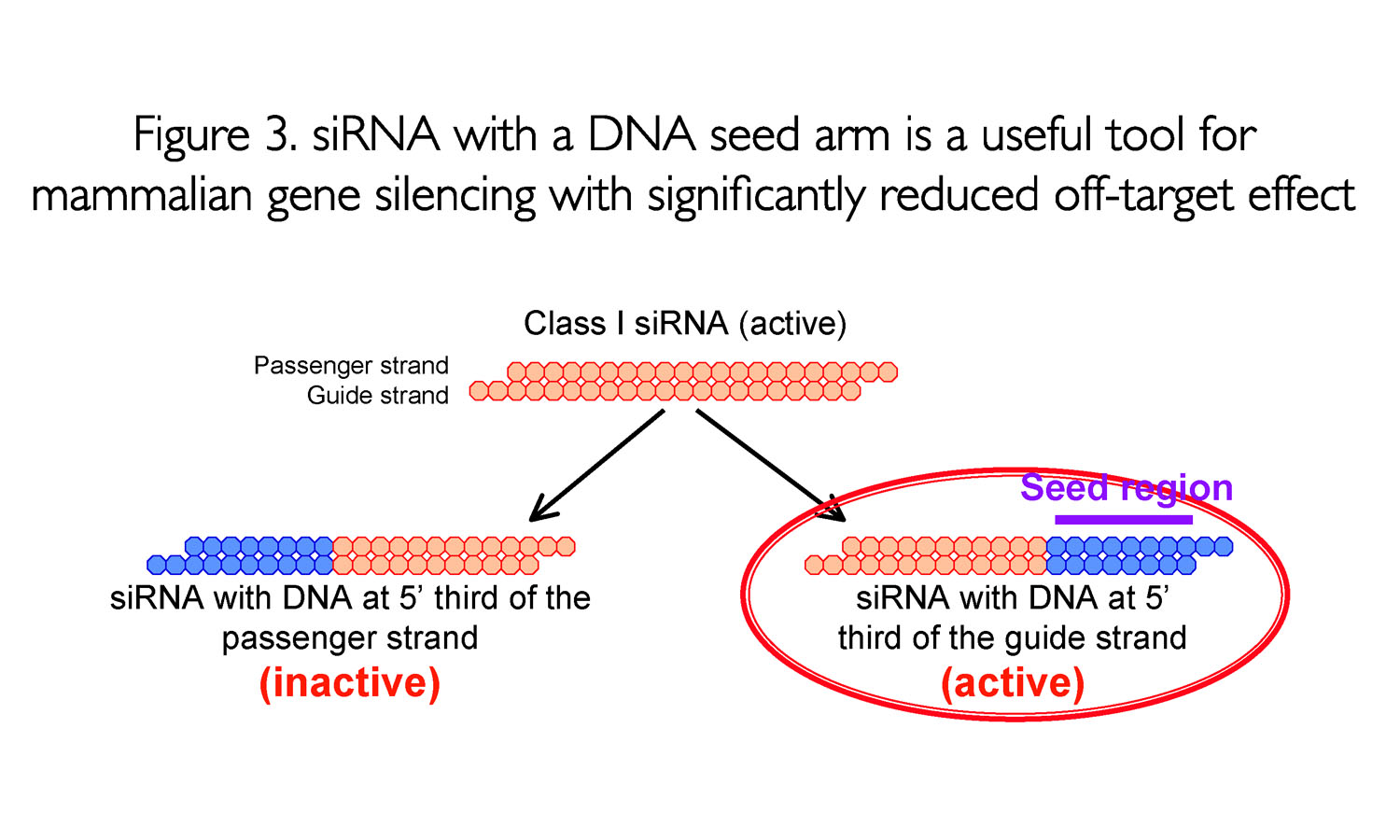
A highly functional siRNA may consist of two regions, the seed duplex region, which is capable of being totally replaced with DNA without substantial loss of gene silencing activity, and the nonseedduplex region, most of which should be RNA and possibly provide binding sites for RNAbinding RLC/RISC proteins To prove the hypothesis that only a molecule with miRNA characteristics (seed region followed by central bulge) can discriminate the two forms of KRAS (pointmutated and WT), we created an siRNA with a sequence identical to amiRKS3, except for the bulge, thus displaying perfect target complementarity, in compliance with siRNA structure andQuirements in the nonseed region of siRNA The nonseed region of siRNA was found to be subdivided into four domains, in which two nucleotide pairs (positions 13 and 14) were replaceable with cognate deoxyribonucleotides without reducing RNAi activity However, RNA sequences at positions 912 and 1518 were essential for effective gene



Small Interfering Rna Sirna Mcmanus Lab
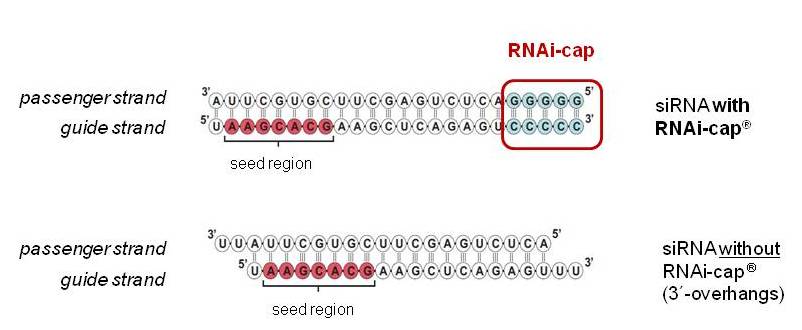



Riboxx Rna Technologies Better Silencing With Rnai Cap
Also, siRNAs are ranked by frequency of potential siRNA seed region matches in the 3'UTR of offtarget transcripts Compared to Silencer siRNA Designs, Silencer Select Designs elicit > 80% target mRNA knockdown, 28% more often Last but not least, Silencer Select siRNAs are modified to enhance specificity the seed region to the siRNA selection criteria (i)–(iv) decreased the percentage of selectable siRNA candidates from 147 to 21%13This means that at least one functional siRNA is selected for just 772% of human genes To overcome such sequence limitations, we evaluated the impact of chemical modifications inUse a few 2'OMe bases in the seed region of the guide strand to decrease the Tm below 215 of this region 2'O methyl base hybridization with RNA has a lower TM (5' end of guide or antisense strand has a seed region of 28 bases that should be AU rich) Modified siRNAs that stabilize AU basepair interactions can induce RNAi 3




Graphical Representation Of Sirna Molecule A Sirna Duplex With Download Scientific Diagram
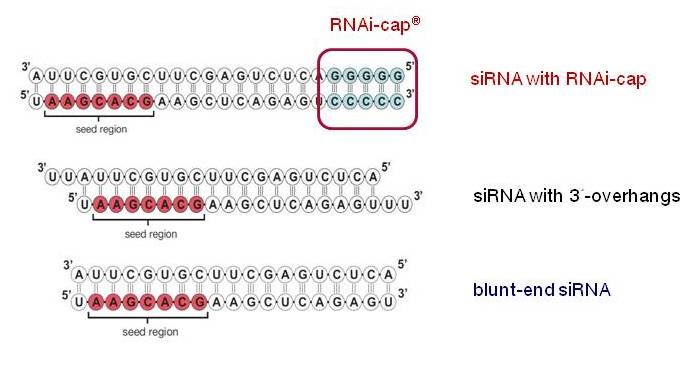



Riboxx Rna Technologies Benefits Of Rnai Cap For Sirna
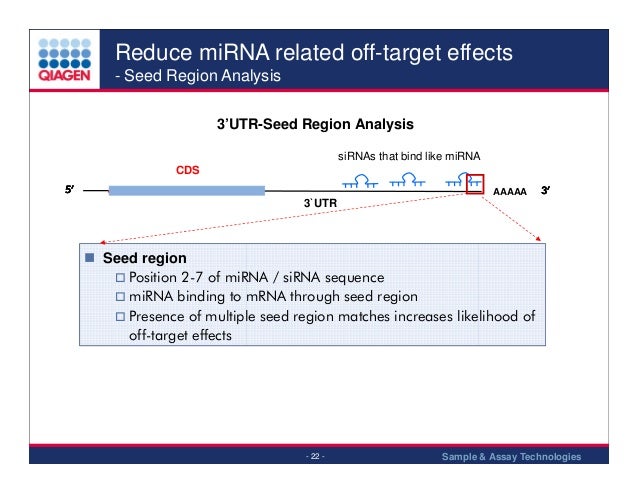
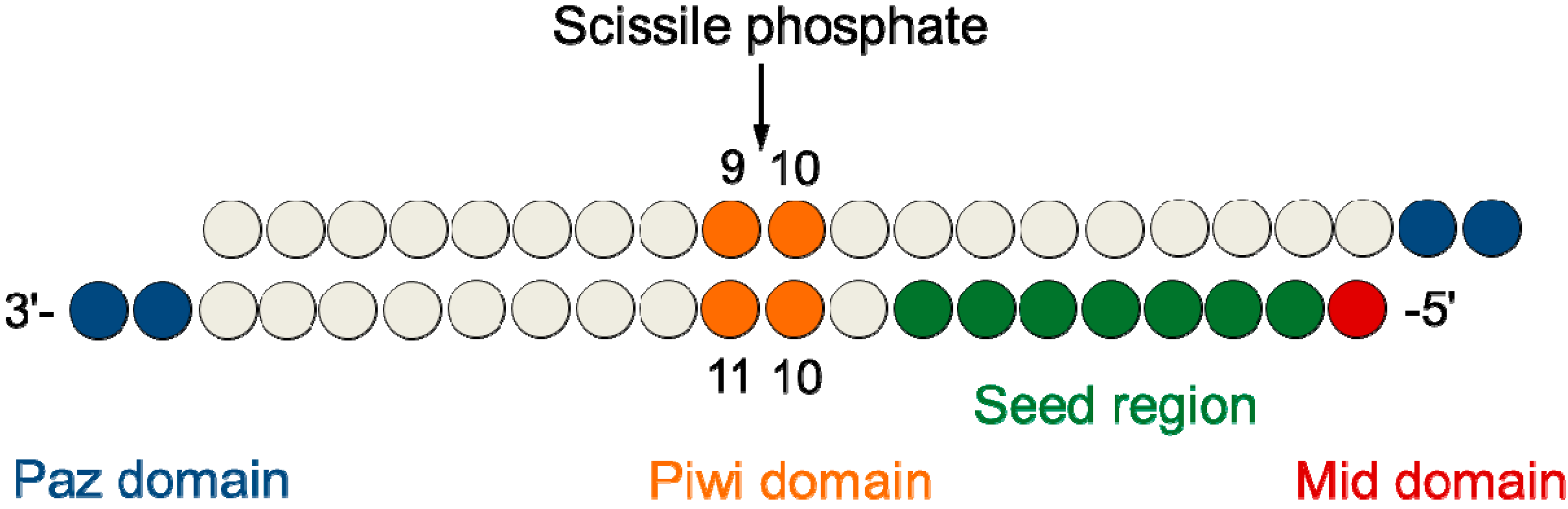
As the offtarget effects were identified based on perfect complementarity to the seed region (positions 2–8) and both terminal nucleotides of siRNA are known to be incorporated into Ago protein (positions 1 and 21), the potential basepairing between siRNA and offtarget mRNA was determined via positions 9– (ie 3' region) The number of GC and AU basepairsSize of seed region of siRNA we proposed is 68 bases Functional alignment Besides general sequence alignment, GenScript siRNA design tool incorporates a novel alignment approach, functional alignment This idea for functional aligment derives from asymmetry of siRNA in the assembly of the RNAi enzyme complexRegion was incapable of inducing offtarget effect Owing to lesser stability of DNA–RNA hybrid than RNA duplex, modified siRNAs with DNA substitution in the seed region were, in most cases, incapable to exert unintended gene silencing due to seed sequence homology Thus, it may be possible to design DNA–RNA chimeras which effec




Figure 5 From Rnai For Treating Hepatitis B Viral Infection Semantic Scholar




Effective Gene Silencing Activity Of Prodrug Type 2 O Methyldithiomethyl Sirna Compared With Non Prodrug Type 2 O Methyl Sirna Bioorganic Medicinal Chemistry Letters X Mol
To avoid off target effect, siRNA Wizard filter candidate siRNA sequence to remove sequence displaying a known miRNA SEED recognition region at 3' end Loop for short hairpin siRNAs (shRNA) We and others have tested a variety of sequences for the loop between the two complementary regions of a shRNA, ranging from 3 to 9 nt in length Collectively, the above experiments demonstrated that downregulated offtargets are enriched in 3′UTRs that are complementary to seed region of both modified siRNA and unmodified siRNA The 2′Omethyl ribosyl modification at position 2 of the guide strand is designed to make seed3′UTR interactions less favorable and does indeed reduceThe bulge modification could better discriminate between on versus offtargets Our results suggest that the bulge
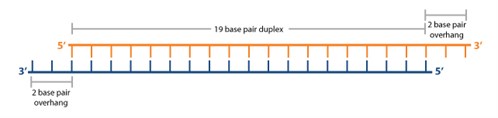



Simax Sirna



1
The seed region of siRNA guide strand and target mRNA (seedtarget duplex) (Figure 1a) Furthermore, we have developed a DNA RNA chimeric siRNA (chiRNA) with deoxyribonucleotides in the 5' proximal eight nucleotides of the guide strand and the complementary nucleotides Incorporation of UNA in the seed region, particularly in position 7, also destabilizes siRNA3′UTR hybridization, 41 and was able to reduce the number of offtarget transcripts by >90% 9, 10 Both methylation and UNA were able to reduce offtargeting without reducing the potency of ontarget silencing 9, 10, 60Our siRNA design algorithms incorporate strategies described by our product scientists in peerreviewed publications1, 2 These groundbreaking methods enhance specificity of silencing by reducing offtarget effects caused by the siRNA seed region Pooling of siRNAs better mimics the natural RNAi pathway and when combined with Thermo Scientific




Shrna And Sirna Of The Same Sequence Regulate The Same Subset Of Download Scientific Diagram




Sirna Versus Mirna As Therapeutics For Gene Silencing Abstract Europe Pmc
SiRNA that successfully targets the same gene18 An additional type of sequencedependent offtarget effect arises from the hexamer seed region, located at positions 2–7 of the siRNA sequence This region can bind to the 3′UTR of various mRNA species and can lead to a complex pattern of mRNA cleavage and translational Thus, the seed region first identifies the target mRNAs, and subsequently form perfect basepairing with intended target mRNA and induce RNAi by Ago2 Based on the mechanism of RNAi, a target genespecific siRNA is considered to be selectable according to the following three steps STEP 1 Selection of Functional siRNA SequenceThe seed region comprises 6 nucleotides in positions 2–7 of the antisense siRNA strand of the siRNA duplex Matches such as these can contribute to downregulation of unintended targets due to the siRNA mimicking the action of an miRNA siRNA designed at QIAGEN is analyzed for 3' UTR/seed region complementarity using a proprietary set of 3' UTR sequences derived from the
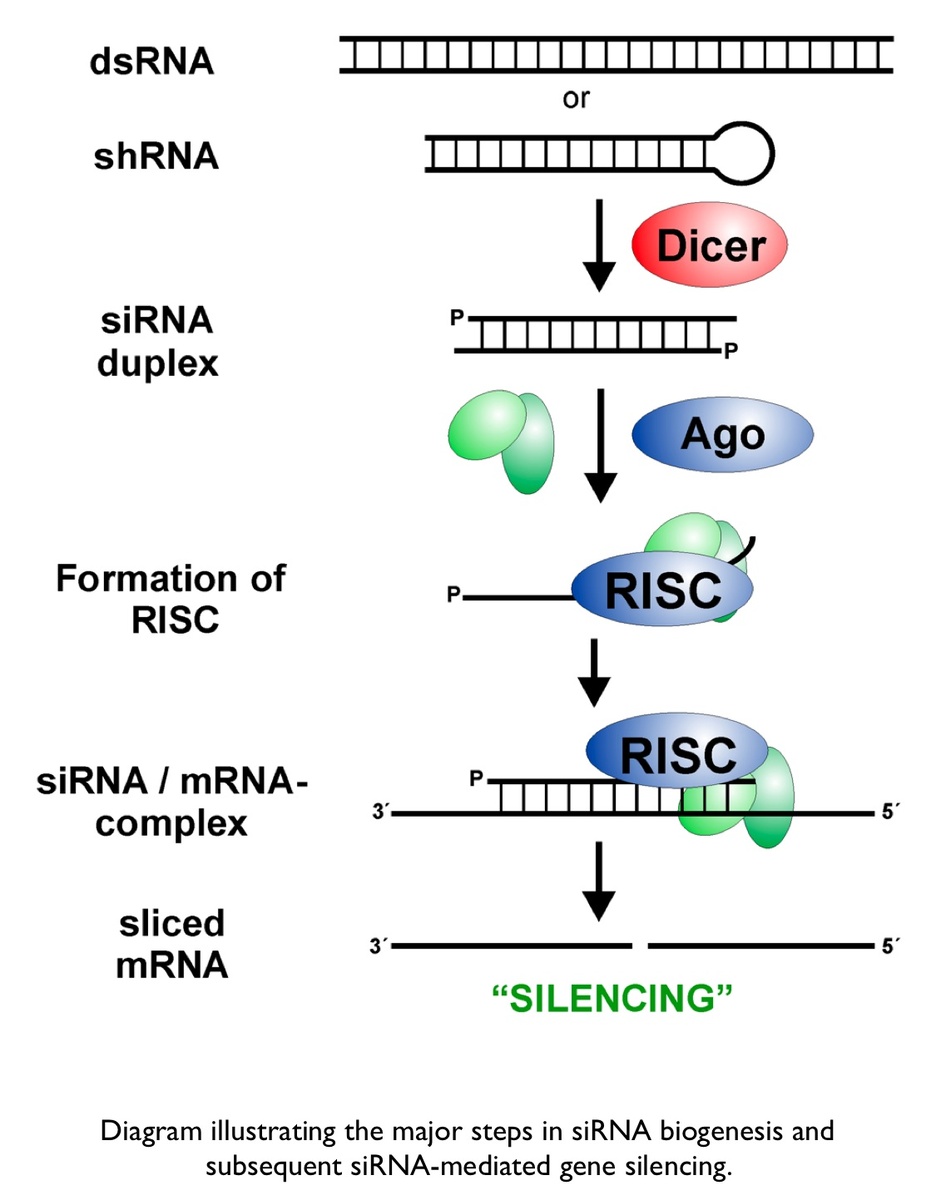



Small Interfering Rna Sirna Mcmanus Lab
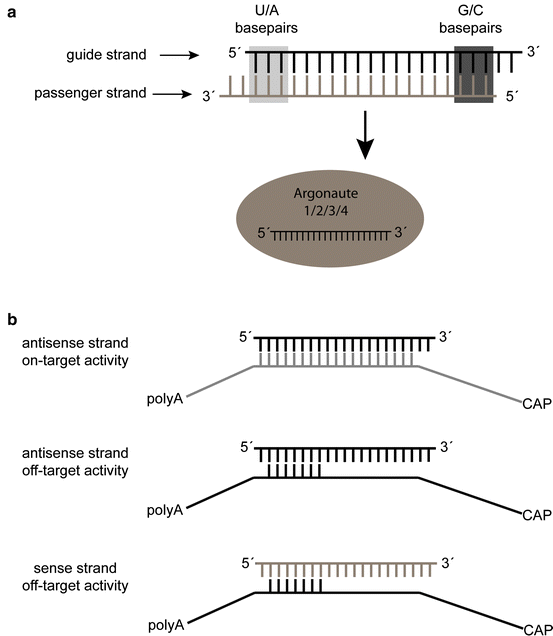



Sirna Design Principles And Off Target Effects Springerlink
The nonseed region of siRNA was found to be subdivided into four domains, in which two nucleotide pairs (positions 13 and 14) were replaceable with cognate deoxyribonucleotides without reducing RNAi activity However, RNA sequences at positions 912 and 1518 were essential for effective gene silencing,Compared with an siRNAlike approach, the requirement of perfect complementarity of the microRNA seed region to a given target sequence in the microRNA/target model has proven to be a more efficient strategy, accomplishing the selective targeting of




Ago Accessible Anticancer Sirnas Designed With Synergistic Mirna Like Activity Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids




Nanomedicines Based On Recombinant Fusion Proteins For Targeting Therapeutic Sirna Oligonucleotides Therapeutic Delivery




Structures Of Sirna A And Dna Seed Containing Sirna B The Download Scientific Diagram




A Simple And Cost Effective Approach For In Vitro Production Of Sliced Sirnas As Potent Triggers For Rnai Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids




Seed Dependant Off Target Effect The Capability Of Sirnas To Induce Download Scientific Diagram




Functional Sirna Sequence And The Mechanism Of Rnai Without Off Target Download Scientific Diagram
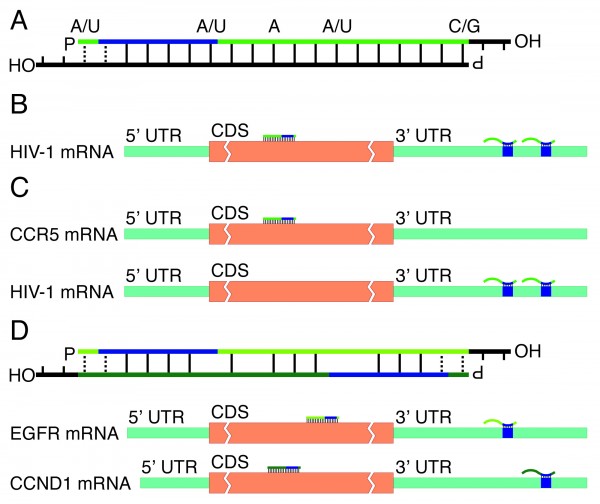



Unconventional Rna Interference Recent Approaches To Robust Rnai European Pharmaceutical Review
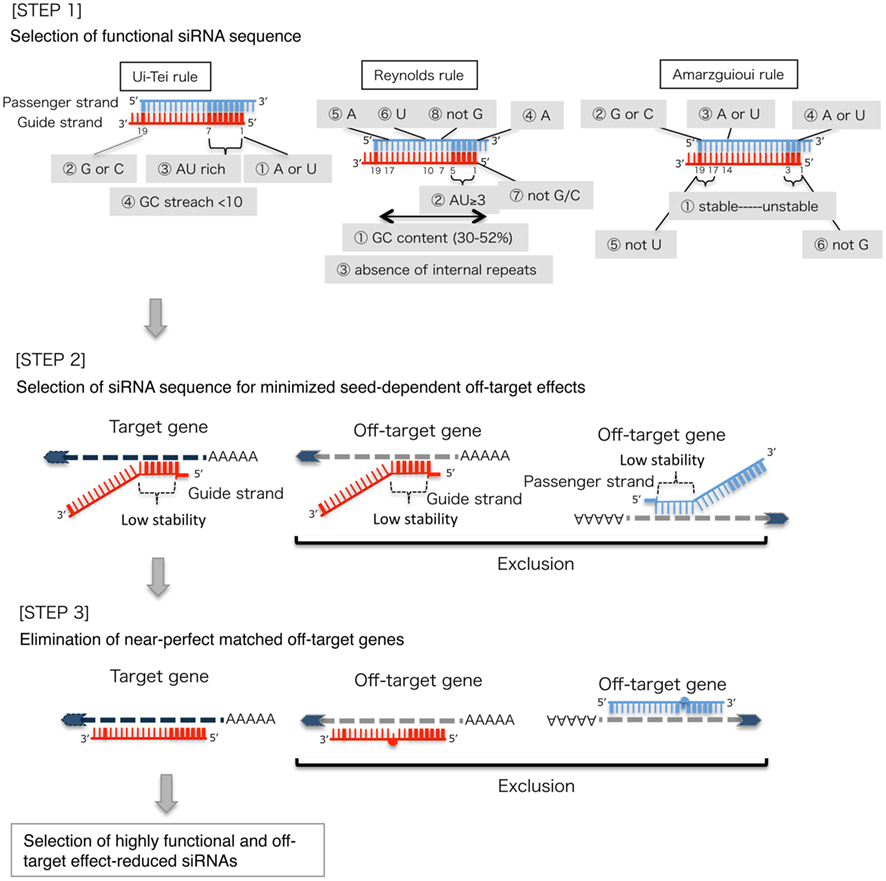



Frontiers Sirna Design Software For A Target Gene Specific Rna Interference Genetics




Selective Targeting Of Point Mutated Kras Through Artificial Micrornas Pnas




Sirna And Rnai Optimization Alagia 16 Wires Rna Wiley Online Library




Effect Of Sugar 2 4 Modifications On Gene Silencing Activity Of Sirna Duplexes Nucleic Acid Therapeutics
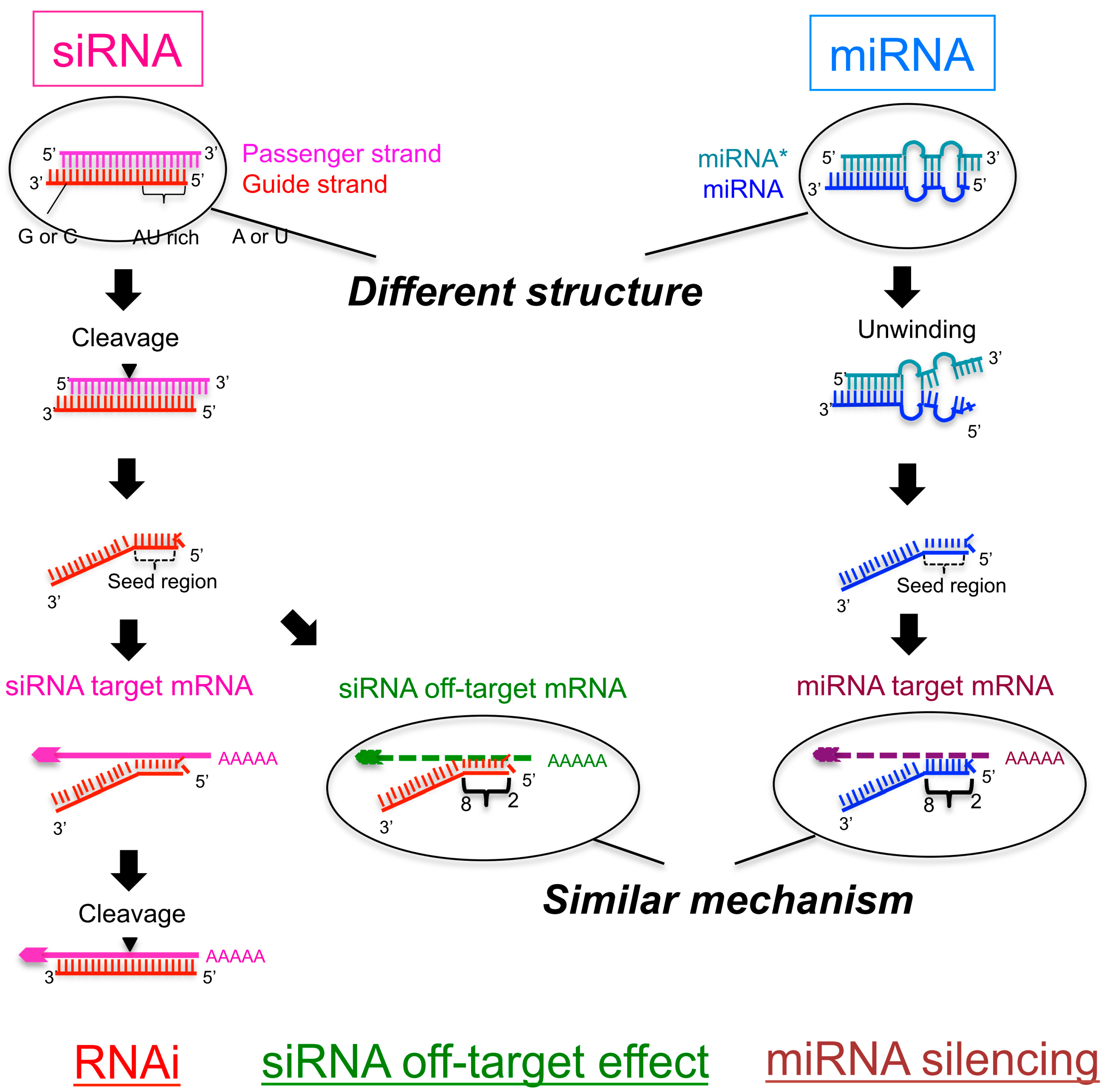



Ijms Free Full Text Is The Efficiency Of Rna Silencing Evolutionarily Regulated Html




Figure 1 From Sdrna Sirna With A Dna Seed For An Efficient And Target Gene Specific Rna Interference Semantic Scholar



Compbio Sirna And Mirna




2 O Methyl At Mer Guide Strand 3 Termini May Negatively Affect Target Silencing Activity Of Fully Chemically Modified Sirna Sciencedirect



Http Ui Tei Rnai Jp Assets Files Pdf 17iribe Acsomega Pdf




Research Ui Tei Lab The University Of Tokyo




Seedseq Off Target Transcriptome Database



Compbio Sirna And Mirna



Www Alnylam De Wp Content Uploads 17 09 Ots 17 Poster 2 Vasant Et Al Pdf



2




Beyond The Seed Structural Basis For Supplementary Microrna Targeting By Human Argonaute2 The Embo Journal




Aspsirna A Resource Of Asp Sirnas Having Therapeutic Potential For Human Genetic Disorders And Algorithm For Prediction Of Their Inhibitory Efficacy G3 Genes Genomes Genetics



Www Longdom Org Open Access Sdrna Sirna With A Dna Seed For An Efficient And Target Gene Specific Rna Interference Gnt Pdf



Research Ui Tei Lab The University Of Tokyo



1



1




Guidelines For The Optimal Design Of Mirna Based Shrnas Abstract Europe Pmc
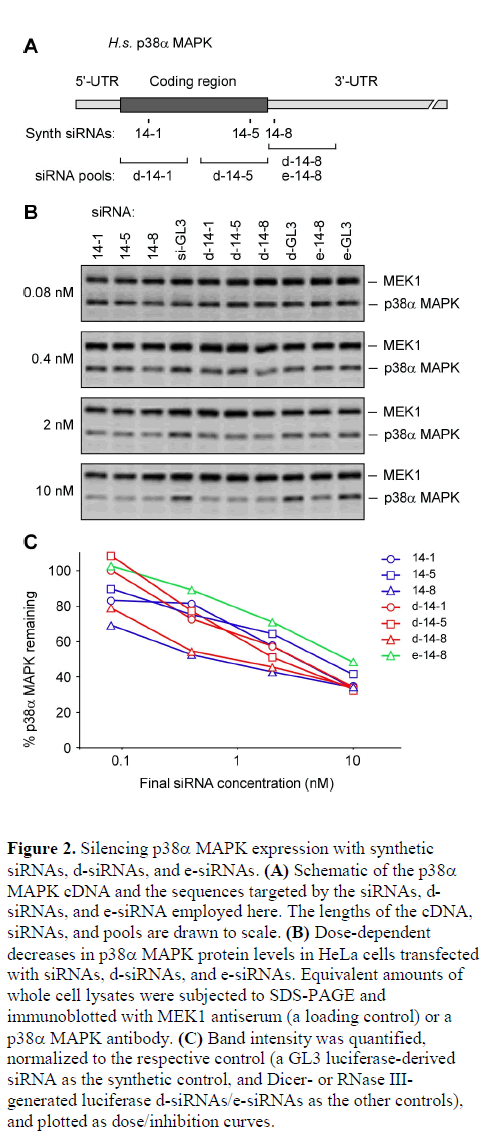



Minimizing Off Target Effects By Using Diced Sirnas For Rna Interference



Sirna And Rnai Pricelist From Gene Link
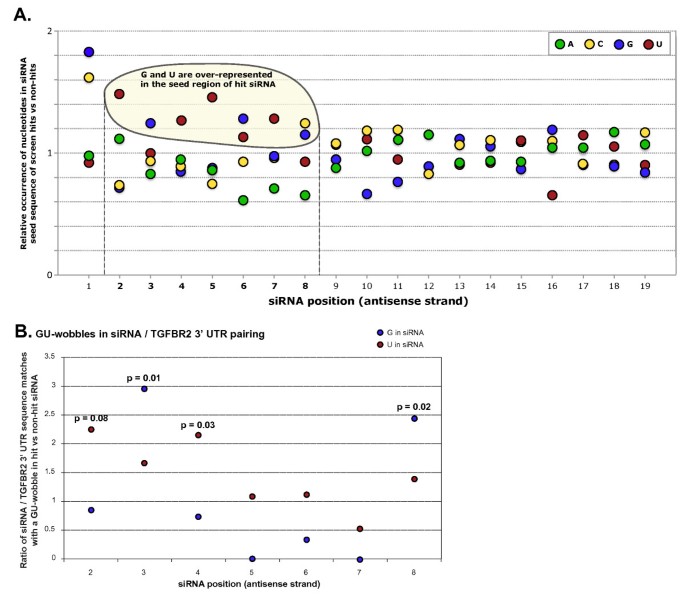



Off Target Effects Dominate A Large Scale Rnai Screen For Modulators Of The Tgf B Pathway And Reveal Microrna Regulation Of Tgfbr2 Silence Full Text




Seed And Non Seed Region Dependent Off Target Effect Analyses For Download Scientific Diagram




Selection Of Chemical Modifications In The Sirna Seed Region That Repress Off Target Effect Springerlink
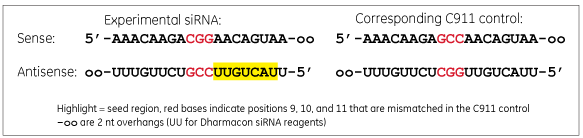



C911 Controls For Sirna Screening




The Loop Position Of Shrnas And Pre Mirnas Is Critical For The Accuracy Of Dicer Processing In Vivo Sciencedirect




Sirnas And Shrnas Tools For Protein Knockdown By Gene Silencing



Frontiers Sirna Finder Si Fi Software For Rnai Target Design And Off Target Prediction Plant Science




Alleviation Of Off Target Effects From Vector Encoded Shrnas Via Codelivered Rna Decoys Pnas



Many Si Shrnas Can Kill Cancer Cells By Targeting Multiple Survival Genes Through An Off Target Mechanism Elife



Sirna And Rnai Pricelist From Gene Link




Small Interfering Rna Wikipedia




Genome Wide Small Interfering Rna Screens Reveal Vamp3 As A Novel Host Factor Required For Uukuniemi Virus Late Penetration Journal Of Virology



Thermo Scientific Dharmacon Sirna Libraries Pdf Free Download



Www Tandfonline Com Doi Pdf 10 1080 14




Passenger Strand Cleavage Facilitates Assembly Of Sirna Into Ago2 Containing Rnai Enzyme Complexes Cell



Sirna Shrna Oligo Optimal Design



Www Sitoolsbiotech Com Pdf Waystoreduceofftargets2 Pdf




Rational Design Of Highly Efficient Artificial Mirna Mirna Download Scientific Diagram



3



Molecules Free Full Text Modulation Of The Rna Interference Activity Using Central Mismatched Sirnas And Acyclic Threoninol Nucleic Acids Atna Units Html
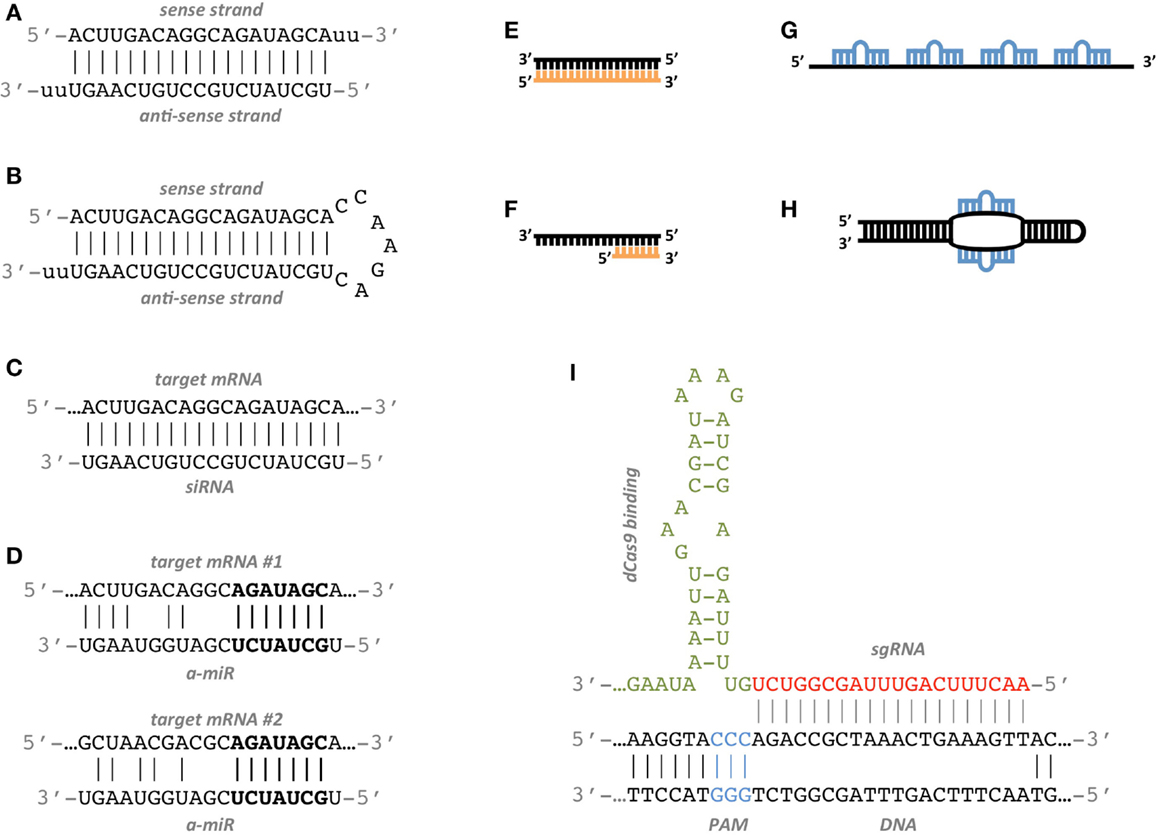



Frontiers Synthetic Rnas For Gene Regulation Design Principles And Computational Tools Bioengineering And Biotechnology



The Sirna Non Seed Region And Its Target Sequences Are Auxiliary Determinants Of Off Target Effects




Pdf New Algorithm For Analysis Of Off Target Effects In Sirna Screens Semantic Scholar




An In Silico Analysis Of Effective Sirnas Against Covid 19 By Targeting The Leader Sequence Of Sars Cov 2 Pandey 21 Advances In Cell And Gene Therapy Wiley Online Library
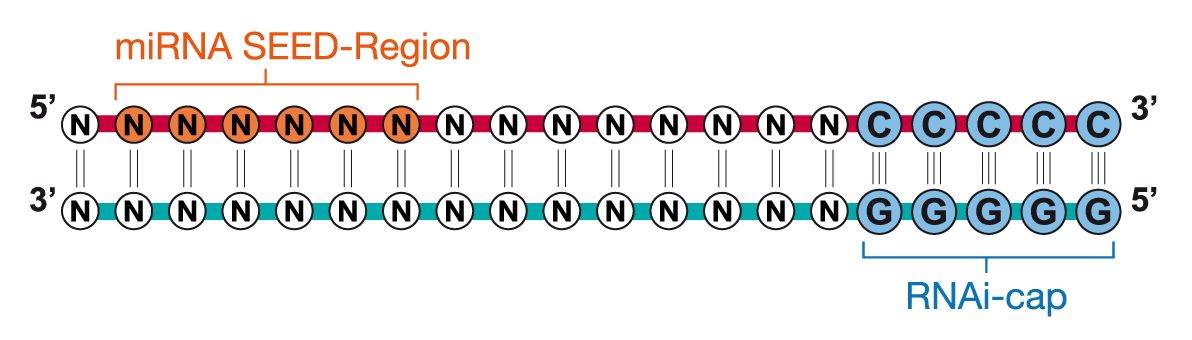



Riboxx Rna Technologies Benefits Of Rnai Cap For Mirna




Small Interfering Rna Wikipedia
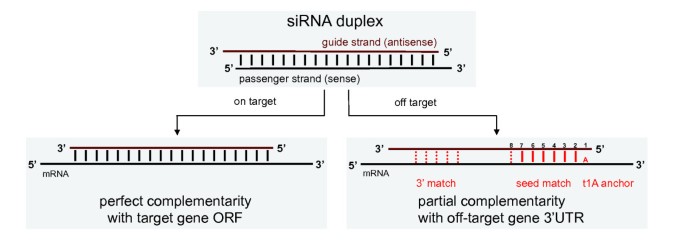



Off Target Effects Dominate A Large Scale Rnai Screen For Modulators Of The Tgf B Pathway And Reveal Microrna Regulation Of Tgfbr2 Silence Full Text




Effective Gene Silencing Activity Of Prodrug Type 2 O Methyldithiomethyl Sirna Compared With Non Prodrug Type 2 O Methyl Sirna Sciencedirect




6mer Seed Toxicity In Tumor Suppressive Micrornas Biorxiv




Rational Design Of Highly Efficient Artificial Mirna Mirna Download Scientific Diagram




6mer Seed Toxicity Determines Strand Selection In Mirnas Biorxiv
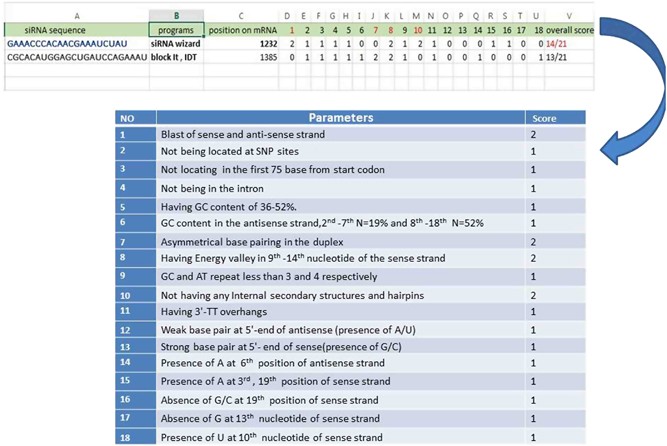



Precise And Efficient Sirna Design A Key Point In Competent Gene Silencing Cancer Gene Therapy



2




Tolerance For Mismatches Between An Sirna And Its Target Sirna Seed Download Scientific Diagram



Http Www Ingentaconnect Com Content Govi Pharmaz 16 Art Crawler True Mimetype Application Pdf



Http Rnajournal Cshlp Org Content 14 5 853 Full Pdf



Www Longdom Org Open Access Sdrna Sirna With A Dna Seed For An Efficient And Target Gene Specific Rna Interference Gnt Pdf




Current Status For Application Of Rna Interference Technology As Nucleic Acid Drug Intechopen



Gess




Seedseq Off Target Transcriptome Database



Frontiers Thermodynamic Control Of Small Rna Mediated Gene Silencing Genetics



New Algorithm For Analysis Of Off Target Effects In Sirna Screens




Sirna Versus Mirna As Therapeutics For Gene Silencing Sciencedirect



The Sirna Non Seed Region And Its Target Sequences Are Auxiliary Determinants Of Off Target Effects Document Gale Academic Onefile



Biological And Physicochemical Characterization Of Sirnas Modified With 2 2 Difluoro 2 Deoxycytidine Gemcitabine New Journal Of Chemistry Rsc Publishing



The Sirna Non Seed Region And Its Target Sequences Are Auxiliary Determinants Of Off Target Effects




Modification Of The Sirna Passenger Strand By 5 Nitroindole Dramatically Reduces Its Off Target Effects Zhang 12 Chembiochem Wiley Online Library
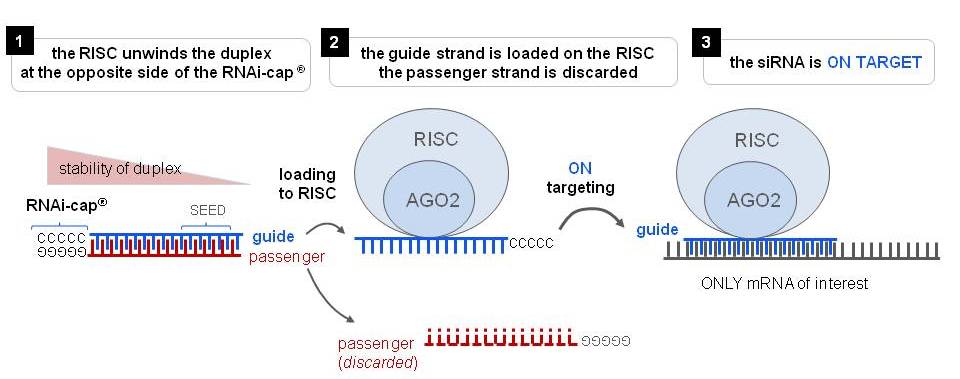



Riboxx Rna Technologies Benefits Of Rnai Cap For Sirna




Sidirect 2 0 Updated Software For Designing Functional Sirna With Reduced Seed Dependent Off Target Effect Springerlink



Part a K Parts Igem Org
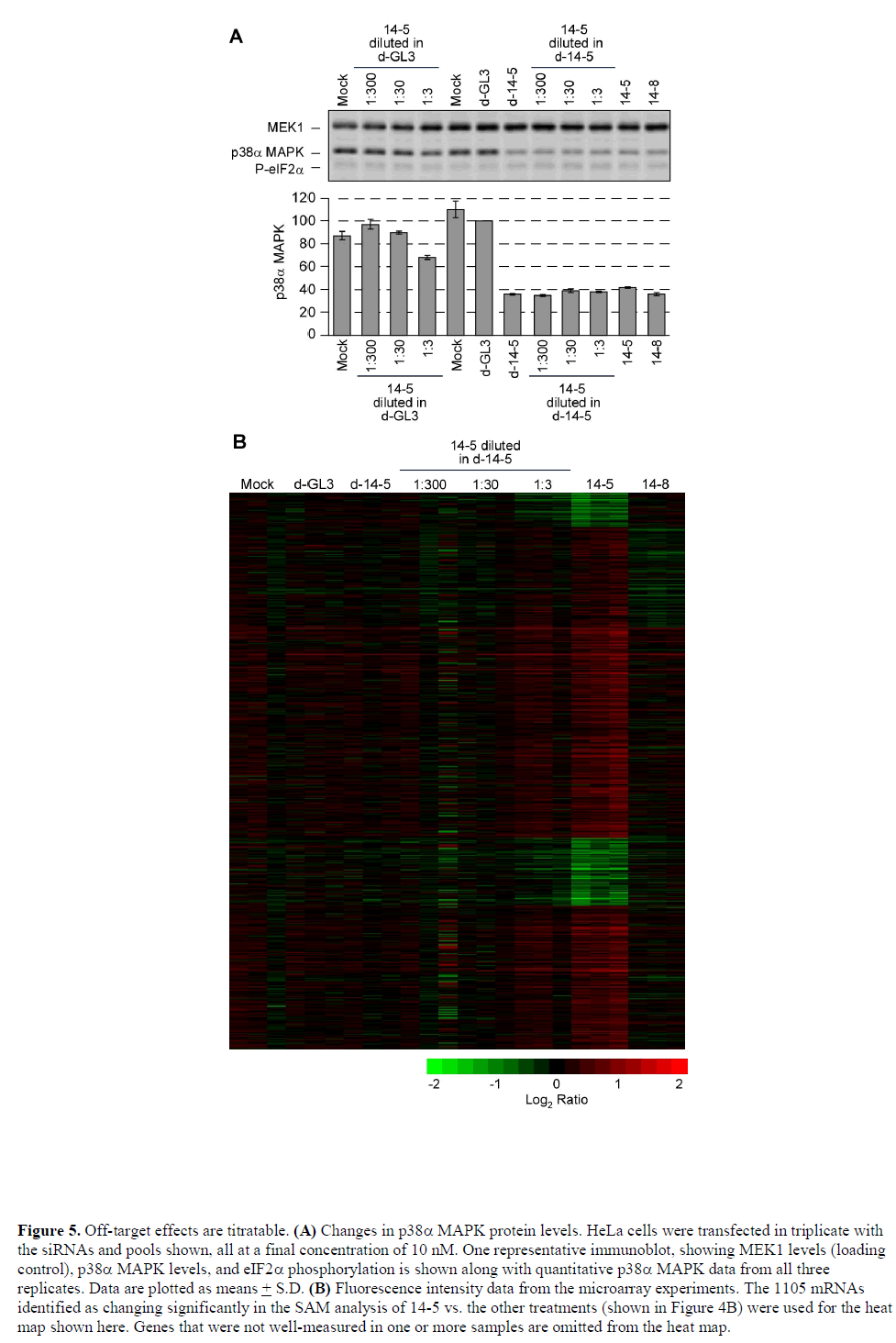



Minimizing Off Target Effects By Using Diced Sirnas For Rna Interference



Www Sitoolsbiotech Com Pdf Waystoreduceofftargets2 Pdf




Many Si Shrnas Can Kill Cancer Cells By Targeting Multiple Survival Genes Through An Off Target Mechanism Elife




Seedseq Off Target Transcriptome Database
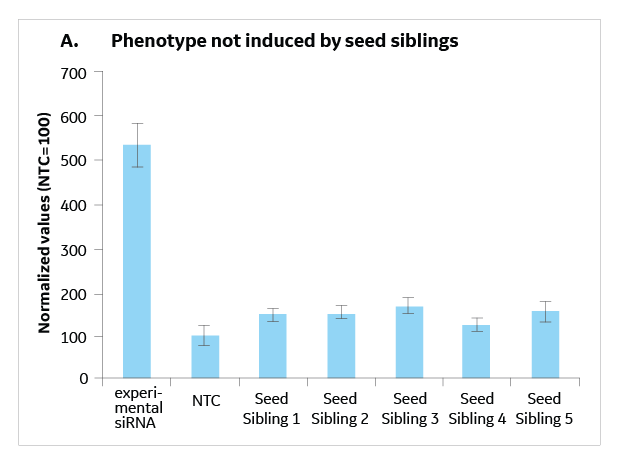



Seed Sibling Controls For Rnai Hit Validation
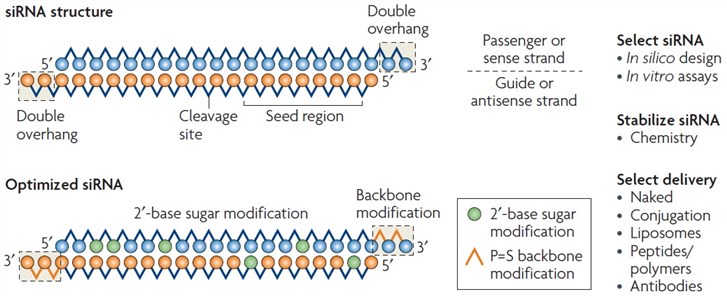



Aln Vsp02 Creative Biolabs



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿